engine oil care
Many people are drivers. but not many are aware of maintenance procedures... the rule of thumb is prevention is better than cure, after all, the purchase of the car is only once off, but the maintenance process goes as long as you keep the car. So one basic factor of maintaining your car is preventive maintenance...
Engine oil in particular is the life line of the engine, like blood in our body, if it's dirty, it'll affect our health... similarly the engine oil works the same way, luckily the engine oil can be changed, but not our blood....
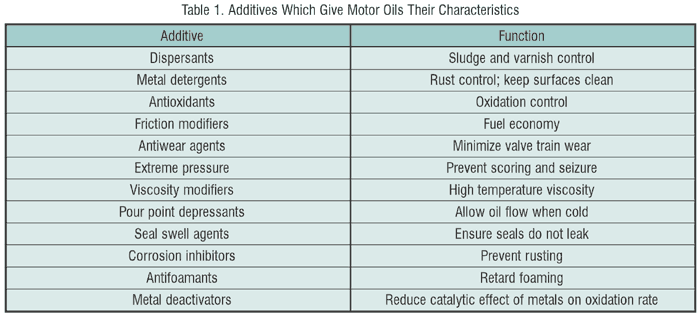
The engine oil has to perform the following:
1) Lubricate
Vehicle engine lubricants are meant to protect the engine from wearing out and from carbon and other contaminants. They form a slippery film between the moving parts and prevent direct metal-to-metal contact and subsequent wear. In an automobile engine there is continous wear and considerable damage. This may lead to sudden or premature engine seizure. Anti wear additives help the oil to maintain the oil film, ensuring protection.
Dirt enters the oil from different sources such as impurities in the fuel and air. It includes carbon deposits, water, sand and tiny particles of metal. Engine oils are fortified with detergents and dispersant components that clean the engine and keep the dirt suspended in the oil, preventing it from settling on the engine parts. When the oil is drained off, it carries the dirt away with it, leaving the engine clean.
2) Engine oil protects
Engine oils contain components that provide protection to the engine parts.
a) Viscosity and viscosity numbers
Viscosity is the relative thickness of the liquid. Viscosity of the lubricant that is suitable for a particular engine depends on the engine design and ambient temperatures. Normally, low temperature environments require low viscosity lubricants (10W, 20W or 30W) and high temperature environments require high viscosity lubricants (40 & 50)
Alternatively some lubricants contain a viscosity modifier that makes them multigrade lubricants (15W/40, 20W/50, 10W/40 etc) These oils are suitable for all weather and eliminate the need to use different oils in different seasons and climatic conditions
b) Detergents to keep the engine clean
Detergent is a chemical present in the engine oil. It helps neutralise the acids form during combustion and keeps the engine surface clean.
c) Dispersant to suspend dirt
Dispersant is a chemical present in the engine oil to keep the dirt suspended and away from the engine surface and to be drained away in the next oil change interval.
d) Anti-wear additives to prevent engine wear
These components are normally present in the engine oil to help the base oil of the lubricant keep the engine free from friction and wear. It forms a slippery layer on the engine parts and allows moving parts to run smoothly.
e) Anti-corrosion and anti-rust
These are helpful in preventing chemical corrosion and rust. Acids and water are the most dangerous by-products of combustion in an internal combustion engines. They may react with the metallic engine parts and lead to corrosion (chemical attack) and rust. Lubricants contain anti-corrosion and anti-rust components that provide protection to the engine parts and prevent damage.
3) Engine oil cools
Engine parts are exposed to high temperature as a results of combustion and friction. One of the main functions of lubricants is to cool the engine and lower these temperatures. The oil, which is cooled by the radiator in turn, cools the engine parts.
4) Engine oil aids Fuel Economy and Enables easy starts
Engine oil can help reduce fuel consumption by reducing friction. Also, multigrade oils (15W/40, 20W/50) are known to help fuel economy better than monogrades (40, 50). These oils maintain higher viscosity at high temperature as compared to the monogrades. They provide the oil film which in necessary to cover the engine parts and prevent drag and friction which rapes the performance and lower fuel efficiency. At a low temperature, multigrade oils have lower viscosity reducing the power required to operate the engine that results in lower fuel consumption.
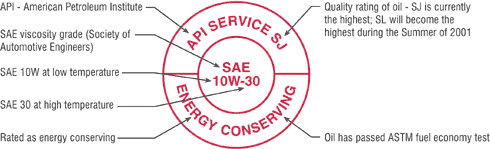
5) American Petroleum Institute (API)
API ratings are the most widely used ratings from an independent organisation governing the grades of the oil based on environmental issues and current engine performance and design. Ensure that the oil that are purchased are displayed with the API donut logo to validate the authenticity and genuinity of the oil. There's also this website - http://eolcs.api.org for users to visit when in doubt of a certain oils' certification. One can check as to whether the oils that claimed to have the API ratings are genuinely certified and approved by the API licensing board.
Bottomline is, the right kind of oil assists in cleaning and protecting the engine from deposited dirt, leakage of fuel, water leakage from radiator, and from the lead and sulphur content that forms part of the fuel. The lube also protects the engine from harmful climatic factors such as humidity and dust. When choosing the appropriate lube for your vehicle, it is important to seek professional advise.
Conclusion
Gasoline engine oils are classified under the API and must meet all requirements to receive the certification demonstrated on oil containers.
Motor oils must perform under difficult environments in both low and high temperature conditions.
New environmental regulations will require new types of engine oil formulations.
Emission regulations and fuel economy will require oils to be lighter in weight and to contain different additives to minimize catalyst damage.
Basestock improvements and new additive technology will be needed to meet future stringent environmental regulations.
Lube basestock and additive suppliers have met the challenge and will continue to do so.
Engine oil in particular is the life line of the engine, like blood in our body, if it's dirty, it'll affect our health... similarly the engine oil works the same way, luckily the engine oil can be changed, but not our blood....
The engine oil has to perform the following:
1) Lubricate
Vehicle engine lubricants are meant to protect the engine from wearing out and from carbon and other contaminants. They form a slippery film between the moving parts and prevent direct metal-to-metal contact and subsequent wear. In an automobile engine there is continous wear and considerable damage. This may lead to sudden or premature engine seizure. Anti wear additives help the oil to maintain the oil film, ensuring protection.
Dirt enters the oil from different sources such as impurities in the fuel and air. It includes carbon deposits, water, sand and tiny particles of metal. Engine oils are fortified with detergents and dispersant components that clean the engine and keep the dirt suspended in the oil, preventing it from settling on the engine parts. When the oil is drained off, it carries the dirt away with it, leaving the engine clean.
2) Engine oil protects
Engine oils contain components that provide protection to the engine parts.
a) Viscosity and viscosity numbers
Viscosity is the relative thickness of the liquid. Viscosity of the lubricant that is suitable for a particular engine depends on the engine design and ambient temperatures. Normally, low temperature environments require low viscosity lubricants (10W, 20W or 30W) and high temperature environments require high viscosity lubricants (40 & 50)
Alternatively some lubricants contain a viscosity modifier that makes them multigrade lubricants (15W/40, 20W/50, 10W/40 etc) These oils are suitable for all weather and eliminate the need to use different oils in different seasons and climatic conditions
b) Detergents to keep the engine clean
Detergent is a chemical present in the engine oil. It helps neutralise the acids form during combustion and keeps the engine surface clean.
c) Dispersant to suspend dirt
Dispersant is a chemical present in the engine oil to keep the dirt suspended and away from the engine surface and to be drained away in the next oil change interval.
d) Anti-wear additives to prevent engine wear
These components are normally present in the engine oil to help the base oil of the lubricant keep the engine free from friction and wear. It forms a slippery layer on the engine parts and allows moving parts to run smoothly.
e) Anti-corrosion and anti-rust
These are helpful in preventing chemical corrosion and rust. Acids and water are the most dangerous by-products of combustion in an internal combustion engines. They may react with the metallic engine parts and lead to corrosion (chemical attack) and rust. Lubricants contain anti-corrosion and anti-rust components that provide protection to the engine parts and prevent damage.

3) Engine oil cools
Engine parts are exposed to high temperature as a results of combustion and friction. One of the main functions of lubricants is to cool the engine and lower these temperatures. The oil, which is cooled by the radiator in turn, cools the engine parts.
4) Engine oil aids Fuel Economy and Enables easy starts
Engine oil can help reduce fuel consumption by reducing friction. Also, multigrade oils (15W/40, 20W/50) are known to help fuel economy better than monogrades (40, 50). These oils maintain higher viscosity at high temperature as compared to the monogrades. They provide the oil film which in necessary to cover the engine parts and prevent drag and friction which rapes the performance and lower fuel efficiency. At a low temperature, multigrade oils have lower viscosity reducing the power required to operate the engine that results in lower fuel consumption.
5) American Petroleum Institute (API)
API ratings are the most widely used ratings from an independent organisation governing the grades of the oil based on environmental issues and current engine performance and design. Ensure that the oil that are purchased are displayed with the API donut logo to validate the authenticity and genuinity of the oil. There's also this website - http://eolcs.api.org for users to visit when in doubt of a certain oils' certification. One can check as to whether the oils that claimed to have the API ratings are genuinely certified and approved by the API licensing board.

Bottomline is, the right kind of oil assists in cleaning and protecting the engine from deposited dirt, leakage of fuel, water leakage from radiator, and from the lead and sulphur content that forms part of the fuel. The lube also protects the engine from harmful climatic factors such as humidity and dust. When choosing the appropriate lube for your vehicle, it is important to seek professional advise.
Conclusion
Gasoline engine oils are classified under the API and must meet all requirements to receive the certification demonstrated on oil containers.
Motor oils must perform under difficult environments in both low and high temperature conditions.
New environmental regulations will require new types of engine oil formulations.
Emission regulations and fuel economy will require oils to be lighter in weight and to contain different additives to minimize catalyst damage.
Basestock improvements and new additive technology will be needed to meet future stringent environmental regulations.
Lube basestock and additive suppliers have met the challenge and will continue to do so.

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home